
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 35-42.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022. 210504
董铮1,2,#, 王雅美3,#, 黎用朝1,2, 熊海波1,2, 薛灿辉1, 潘孝武1,2, 刘文强1,2, 魏秀彩1,2, 李小湘1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-24
修回日期:2021-08-16
出版日期:2022-01-10
发布日期:2022-01-10
通讯作者:
李小湘
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者;
基金资助:
DONG Zheng1,2,#, WANG Yamei3,#, LI Yongchao1,2, XIONG Haibo1,2, XUE Canhui1, PAN Xiaowu1,2, LIU Wenqiang1,2, WEI Xiucai1,2, LI Xiaoxiang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-05-24
Revised:2021-08-16
Online:2022-01-10
Published:2022-01-10
Contact:
LI Xiaoxiang
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to the work;
摘要:
【目的】基于水稻MAGIC-Hei(Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross)群体,在多环境下挖掘镉含量相关新位点/基因,并筛选含有低镉等位基因的优良株系,为选育低镉积累品种提供新的基因和种质资源。【方法】将由8个亲本衍生的MAGIC群体分别于2017、2018、2019和2020年度种植于湖南长沙并开展稻米镉含量表型测试分析。利用GBS(genotyping by sequencing)简化基因组测序获得基因型数据,对稻米镉含量开展全基因组关联分析(genome-wide association analysis,GWAS),发掘QTL位点,解析其遗传机制。【结果】检测到了14个镉积累相关的QTL位点,除了第8染色体之外,其他11条染色体上均有分布。其中6个位点与已报道基因一致,8个为新发现位点。另外,这8个位点分布在第2、4、7、9和12染色体上,均可以在两个及以上环境中检测到,效应较为稳定,可用于下一步精细定位及功能研究。结合基因注释和基因表达分析结果,推测LOC_Os02g37160、LOC_Os02g49560、LOC_Os04g39010和LOC_Os06g46310为镉含量相关位点候选基因,这些基因与重金属转运和积累等功能相关。另外,我们筛选到10个携带有利等位基因的优良株系,可用于低镉积累水稻材料的创制。【结论】发掘了8个水稻镉积累相关性状的QTL位点和低镉优异材料,对于镉积累相关遗传研究和利用分子标记辅助选育低镉积累品种具有一定意义。
董铮, 王雅美, 黎用朝, 熊海波, 薛灿辉, 潘孝武, 刘文强, 魏秀彩, 李小湘. 基于MAGIC群体的水稻镉含量全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 35-42.
DONG Zheng, WANG Yamei, LI Yongchao, XIONG Haibo, XUE Canhui, PAN Xiaowu, LIU Wenqiang, WEI Xiucai, LI Xiaoxiang. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Cadmium Content in Rice Based on MAGIC Population[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 35-42.
| 年份 Year | 亲本 Parent | 多亲本高世代互交群体MAGIC population | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 变异系数 CV/% | |
| 2017 | 0.889 | 0.528 | 1.070 | 1.338 | 0.542 | 1.412 | 0.527 | 0.514 | 0.651±0.184 a | 0.148~1.336 | 28.26 |
| 2018 | 1.239 | 0.579 | 1.667 | 1.254 | 0.949 | 1.140 | 0.841 | 0.845 | 0.672±0.226 ab | 0.068~1.516 | 33.63 |
| 2019 | 0.605 | 0.291 | 0.627 | 0.823 | 0.491 | 0.443 | 0.459 | 0.509 | 0.327±0.154 c | 0.070~1.188 | 47.10 |
| 2020 | 0.944 | 0.509 | 0.903 | 0.739 | 0.288 | 0.554 | 0.380 | 0.532 | 0.534±0.160 b | 0.192~1.125 | 29.96 |
Table 1 Analysis on the cadmium content in MAGIC-Hei under various environments.
| 年份 Year | 亲本 Parent | 多亲本高世代互交群体MAGIC population | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 变异系数 CV/% | |
| 2017 | 0.889 | 0.528 | 1.070 | 1.338 | 0.542 | 1.412 | 0.527 | 0.514 | 0.651±0.184 a | 0.148~1.336 | 28.26 |
| 2018 | 1.239 | 0.579 | 1.667 | 1.254 | 0.949 | 1.140 | 0.841 | 0.845 | 0.672±0.226 ab | 0.068~1.516 | 33.63 |
| 2019 | 0.605 | 0.291 | 0.627 | 0.823 | 0.491 | 0.443 | 0.459 | 0.509 | 0.327±0.154 c | 0.070~1.188 | 47.10 |
| 2020 | 0.944 | 0.509 | 0.903 | 0.739 | 0.288 | 0.554 | 0.380 | 0.532 | 0.534±0.160 b | 0.192~1.125 | 29.96 |
| QTL 名称 | 环境 Environment | 染色体Chromosome | 优异等位基因 Allele | 位置 Position/Mb | 峰值SNP Peak SNP | P值 P-value | 贡献率 R2/% | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qCd1.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 1 | G | 20.9-22.0 | rs1_21942515 | 5.3×10-4 | 8.26 | [20] |
| qCd2.1 | E4 | 2 | G | 23.8-24.3 | S2_23819612 | 1.7×10-4 | 8.53 | |
| qCd2.2 | E2 | 2 | A | 30.1 | rs2_30102654 | 9.4×10-4 | 6.62 | |
| qCd3.1 | E2/E3 | 3 | A | 5.8-6.9 | S3_5834039 | 3.4×10-4 | 7.40 | [21] |
| qCd4.1 | E2/E3/E4 | 4 | T | 20.2-24.2 | S4_20195543 | 4.4×10-4 | 7.46 | |
| qCd5.1 | E1/E3 | 5 | C | 1.7-2.1 | rs5_1811027 | 2.9×10-4 | 7.27 | OsMTP1[22] |
| qCd6.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 6 | C | 27.0-30.8 | S6_27300620 | 2.6×10-5 | 10.57 | OsHMA2[23] |
| qCd7.1 | E3/E4 | 7 | C | 14.5-17.1 | S7_16945471 | 6.8×10-5 | 9.11 | |
| qCd9.1 | E1/E2 | 9 | C | 8.1-9.8 | rs9_9777578 | 6.9×10-5 | 9.64 | |
| qCd9.2 | E1 | 9 | G | 12.2-12.8 | rs9_12209561 | 3.0×10-4 | 8.00 | |
| qCd9.3 | E4 | 9 | G | 16.6-16.8 | S9_16720741 | 4.1×10-4 | 7.53 | [24] |
| qCd10.1 | E3 | 10 | C | 15.9 | S10_15856776 | 2.7×10-4 | 7.66 | |
| qCd11.1 | E3/E4 | 11 | G | 17.6-18.0 | S11_17883239 | 1.3×10-4 | 8.77 | [25] |
| qCd12.1 | E3 | 12 | G | 8.0-8.2 | S12_8031425 | 9.7×10-5 | 8.73 |
表2 MAGIC-Hei群体中通过全基因组关联分析检测到与镉积累显著关联的位点
Table 2 Loci for cadmium content by GWAS in MAGIC-Hei.
| QTL 名称 | 环境 Environment | 染色体Chromosome | 优异等位基因 Allele | 位置 Position/Mb | 峰值SNP Peak SNP | P值 P-value | 贡献率 R2/% | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qCd1.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 1 | G | 20.9-22.0 | rs1_21942515 | 5.3×10-4 | 8.26 | [20] |
| qCd2.1 | E4 | 2 | G | 23.8-24.3 | S2_23819612 | 1.7×10-4 | 8.53 | |
| qCd2.2 | E2 | 2 | A | 30.1 | rs2_30102654 | 9.4×10-4 | 6.62 | |
| qCd3.1 | E2/E3 | 3 | A | 5.8-6.9 | S3_5834039 | 3.4×10-4 | 7.40 | [21] |
| qCd4.1 | E2/E3/E4 | 4 | T | 20.2-24.2 | S4_20195543 | 4.4×10-4 | 7.46 | |
| qCd5.1 | E1/E3 | 5 | C | 1.7-2.1 | rs5_1811027 | 2.9×10-4 | 7.27 | OsMTP1[22] |
| qCd6.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 6 | C | 27.0-30.8 | S6_27300620 | 2.6×10-5 | 10.57 | OsHMA2[23] |
| qCd7.1 | E3/E4 | 7 | C | 14.5-17.1 | S7_16945471 | 6.8×10-5 | 9.11 | |
| qCd9.1 | E1/E2 | 9 | C | 8.1-9.8 | rs9_9777578 | 6.9×10-5 | 9.64 | |
| qCd9.2 | E1 | 9 | G | 12.2-12.8 | rs9_12209561 | 3.0×10-4 | 8.00 | |
| qCd9.3 | E4 | 9 | G | 16.6-16.8 | S9_16720741 | 4.1×10-4 | 7.53 | [24] |
| qCd10.1 | E3 | 10 | C | 15.9 | S10_15856776 | 2.7×10-4 | 7.66 | |
| qCd11.1 | E3/E4 | 11 | G | 17.6-18.0 | S11_17883239 | 1.3×10-4 | 8.77 | [25] |
| qCd12.1 | E3 | 12 | G | 8.0-8.2 | S12_8031425 | 9.7×10-5 | 8.73 |
| 候选基因 Candidate gene | 注释信息 Annotation |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g37160 | 重金属转运蛋白Heavy metal transport/detoxification protein, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os02g49560 | bZIP转录因子bZIP transcription factor domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os04g39010 | 重金属相关结构域蛋白Heavy metal associated domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os06g46310 | 重金属转运因子Nramp6 Metal transporter Nramp6, putative, expressed |
表3 水稻镉含量相关候选基因
Table 3 Candidate genes for rice cadmium content.
| 候选基因 Candidate gene | 注释信息 Annotation |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g37160 | 重金属转运蛋白Heavy metal transport/detoxification protein, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os02g49560 | bZIP转录因子bZIP transcription factor domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os04g39010 | 重金属相关结构域蛋白Heavy metal associated domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os06g46310 | 重金属转运因子Nramp6 Metal transporter Nramp6, putative, expressed |
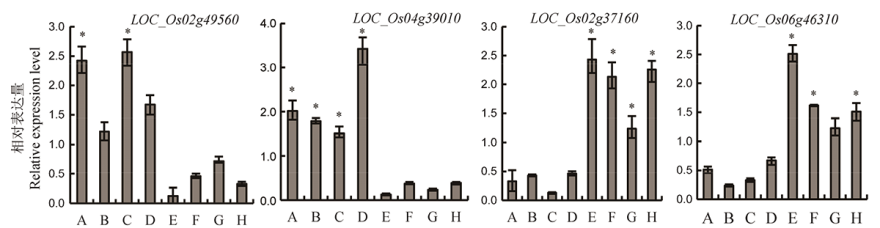
图4 候选基因在MAGIC-Hei不同亲本间的表达量差异 A, Fedearroz 50; B, IR 84196-12-32 (SAMBHA MAHSURI+SUB1); C, R64633-87-2-2-3-3 (PSBRc82); D, IR4630-22-2-5-1-3; E, IR45427-2B-2-2B-1-1; F, Shan-Huang Zhan-2 (SHZ-2); G, IR77298-14-1-2-10; H, IR77186-122-2-2-3(PSBRc 158). A~D为高镉亲本,E~F为低镉亲本。内参基因为β-Actin。*表示在P<0.05水平上显著相关(n≥3)。
Fig. 4. Expression difference of candidate genes among different parents in MAGIC-Hei. A-D are high Cd content parents, E-F are low Cd content parents. The internal reference gene is β-Actin. *Significant correlation at P<0.05 (n≥3).
| [1] | Canli M, Furness R W. Toxicity of heavy metals dissolved in sea water and influences of sex and size on metal accumulation and tissue distribution in the norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 1993,36(4):217-236. |
| [2] | Grant C A, Clarke J M, Duguid S, Chaney R L. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008,390(2/3):301-310. |
| [3] | Yao H, Xu J, Huang C. Substrate utilization pattern, biomass and activity of microbial communities in a sequence of heavy metal-polluted paddy soils[J]. Geoderma, 2003,115(1):139-148. |
| [4] | Li Z, Ma Z, der Kuijp T J, Yuan Z, Huang L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468-469:843-853. |
| [5] | Clemens S, Aarts M G, Thomine S, Verbruggen N. Plantscience: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2013,18(2):92-99. |
| [6] | 丁仕林, 刘朝雷, 钱前, 高振宇. 水稻重金属镉吸收和转运的分子遗传机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019,33(5):383-390. |
| Ding S L, Liu C L, Qian Q, Gao Z Y. Research advances on molecular genetic mechanism for Cadmium absorption and transportation in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019,33(5):383-390. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: Perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation[J]. Rice, 2012,5(1):1-8. |
| [8] | Kashiwagi T, Shindoh K, Hirotsu N, Ishimaru K. Evidence for separate translocation pathways in determining cadmium accumulation in grain and aerial plant parts in rice[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2009,9(8):1-10. |
| [9] | Huang D R, Fan Y Y, Hu B L, Xiao Q Y, Chen D Z, Zhuang J Y. Assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal content in rice grain using an Oryza sativa×O. rufipogon backcross inbred line population[J]. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 2018,98(4):1339-1345. |
| [10] | Zhao K, Tung C, Eizenga G C, Wright M H, Ali M L, Price A H, Norton G J, Islam M R, Reynolds A, Mezey J, McClung A M, Bustamante C D, McCouch S R. Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa L[J]. Nature Communications, 2011,2(1):467. |
| [11] | Liu J D, He Z H, Rasheed A, Wen W E, Yan J, Zhang P Z, Wan Y X, Xie C J, Xia X C. Genome-wide association mapping of black point reaction in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2017,17(1):220-232. |
| [12] | Elshire R J, Glaubitz J C, Sun Q, Poland J A, Kawamoto K, Buckler E S, Mitchell S E. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species[J]. PloS ONE, 2011,6(5):e19379. |
| [13] | Bandillo N, Raghavan C, Muyco P A, Sevilla M A L, Lobina I T, Dilla-Ermita C J, Tung C W, McCouch S, Thomson M, Mauleon R, Singh R K, Gregorio G, Redoña E, Leung H. Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross (MAGIC) populations in rice: Progress and potential for genetics research and breeding[J]. Rice, 2013,6(1):1-15. |
| [14] | Raghavan C, Mauleon R, Lacorte V, Jubay M, Zaw H, Bonifacio J, Singh R K, Huang B E, Leung H. Approaches in characterizing genetic structure and mapping in a rice multiparental population[J]. Genes Genome Genetics, 2017,7(6):1721-1730. |
| [15] | Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles[J]. New Phytologist, 2011,189(1):190-199. |
| [16] | Luo J, Huang J, Zeng D, Peng J S, Zhang G B, Ma H L, Guan Y, Yi H Y, Fu Y L, Lin H X, Qian Q, Gong J M. A defensin-like protein drives cadmium efflux and allocation in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018,9(1):645. |
| [17] | Yan H, Xu W, Xie J, Gao Y W, Wu L L, Sun L, Feng L, Chen X, Zhang T, Dai C H, Li T, Lin X N, Zhang Z Y, Wang X Q, Li F M, Zhu X Y, Li J J, Li Z C, Chen C Y, Ma M, Zhang H L, He Z Y. Variation of a major facilitator superfamily gene contributes to differential cadmium accumulation between rice subspecies[J]. Nature Communications, 2019,10(1):1-12. |
| [18] | Chen J, Huang X, Salt D E, Zhao F J. Mutation in OsCADT1 enhances cadmium tolerance and enriches selenium in rice grain[J]. New Phytologist, 2020,226(3):838-850. |
| [19] | Tang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Li M, Wang Q, Tian F, Su Z, Pan Y, Liu D, Lipka A E, Buckler E S, Zhang Z. GAPIT Version 2: An enhanced integrated tool for genomic association and prediction[J]. Plant Genome, 2016 9(2):1-9. |
| [20] | Xu Q, Zheng T Q, Hu X, Cheng L R, Xu J L, Shi Y M, Li Z K. Examining two sets of introgression lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.) reveals favorable alleles that improve grain Zn and Fe concentrations[J]. PloS ONE, 2015,10(7):e0131846 |
| [21] | Zhang M, Pinson S R M, Tarpley L, Huang X Y, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Baxter I, Guerinot M L, Salt D E. Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2014,127(1):137-165. |
| [22] | Yuan L, Yang S, Liu B, Zhang M, Wu K. Molecular characterization of a rice metal tolerance protein, OsMTP1[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2012,31(1):67-79 |
| [23] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Ogo Y, Senoura T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2012,35(11):1948-1957. |
| [24] | Yan Y F, Lesta I P, Lee K J, Kim M Y, Lee S H, Lee B W. Identification of quantitative trait loci for cadmium accumulation and distribution in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Genome, 2013,56(4):227-232. |
| [25] | 陈志德. 水稻不同品种耐镉性鉴定及耐镉胁迫相关性状的QTL定位[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010 |
| Chen Z D. Screening of rice varieties with cadmium tolerance and mapping of QTLs related to cadmium stress in rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010 | |
| [26] | 陈艳彩, 唐文帮. 筛选和培育镉低积累水稻品种的进展和问题探讨[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2018,39(6):1044-1051 |
| Chen C Y, Tang W B. A perspective on the selection and breeding of low-Cd rice[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2018,39(6):1044-1051. | |
| [27] | Lan H, Wang Z, Wang Q H, Wang M M, Bao Y M, Huang J, Zhang H S. Characterization of a vacuolar zinc transporter OsZT1 in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2013,40(2):1201-1210. |
| [28] | 鄂志国, 张玉屏, 王磊. 水稻镉胁迫应答分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013,27(5):539-544. |
| E Z G, Zhang Y P, Wang L. Molecular mechanism of rice responses to cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013,27(5):539-544. (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [1] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [2] | 侯本福, 杨传铭, 张喜娟, 杨贤莉, 王立志, 王嘉宇, 李红宇, 姜树坤. 利用龙稻5号/中优早8号RIL群体定位粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 13-24. |
| [3] | 胡佳晓, 刘进, 崔迪, 勒思, 周慧颖, 韩冰, 孟冰欣, 余丽琴, 韩龙植, 马小定, 黎毛毛. 利用东乡野生稻染色体片段置换系鉴定穗部性状主效QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 597-608. |
| [4] | 谢开珍, 张建明, 程灿, 周继华, 牛付安, 孙滨, 张安鹏, 闻伟军, 代雨婷, 胡启琰, 邱越, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 低直链淀粉含量水稻种质资源的鉴定与QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 609-616. |
| [5] | 姚晓云, 陈春莲, 熊运华, 黄永萍, 彭志勤, 刘进, 尹建华. 水稻加工和外观品质性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 507-517. |
| [6] | 韦敏益, 马增凤, 黄大辉, 秦媛媛, 刘驰, 卢颖萍, 罗同平, 李振经, 张月雄, 秦钢. 基于QTL-Seq的水稻抗细菌性条斑病QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. |
| [7] | 黄涛, 王燕宁, 钟奇, 程琴, 杨朦朦, 王鹏, 吴光亮, 黄诗颖, 李才敬, 余剑峰, 贺浩华, 边建民. 利用染色体片段置换系群体定位和分析水稻粒重和粒型QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| [8] | 李杰, 田蓉蓉, 白天亮, 朱春艳, 宋佳伟, 田蕾, 马帅国, 吕建东, 胡慧, 王震宇, 罗成科, 张银霞, 李培富. 水稻回交群体剑叶性状综合评价及QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 573-585. |
| [9] | 陈喜娜, 袁泽科, 胡珍珍, 赵全志, 孙红正. 利用QTL-Seq定位粳稻整精米率QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 449-454. |
| [10] | 杜成兴, 张华丽, 戴冬青, 吴明月, 梁敏敏, 陈俊宇, 马良勇. 水稻粒重粒形QTL的定位及qTGW1.2/qGL1.2的验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 359-372. |
| [11] | 朱玉君, 左紫薇, 张振华, 樊叶杨. 一种水稻微效QTL精细定位和克隆新途径[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. |
| [12] | 刘维, 陆展华, 卢东柏, 王晓飞, 王石光, 薛皦, 何秀英. 水稻小穗簇生基因OsCL6的定位及候选基因分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 238-248. |
| [13] | 季芝娟, 曾宇翔, 梁燕, 杨长登. 水稻恶苗病抗性研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 1-10. |
| [14] | 农保选, 秦碧霞, 夏秀忠, 杨行海, 张宗琼, 曾宇, 邓国富, 蔡健和, 李战彪, 刘丕庆, 李丹婷. 南方水稻黑条矮缩病抗性的遗传分析及主效QTL的精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 135-143. |
| [15] | 周梦玉, 宋昕蔚, 徐静, 付雪, 李婷, 朱雨晨, 肖幸运, 毛一剑, 曾大力, 胡江, 朱丽, 任德勇, 高振宇, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 吴明国, 林建荣, 张光恒. 籼稻C84和粳稻春江16B重组自交系遗传图谱构建及籽粒性状QTL定位与验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 207-218. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||